Why Semi-Autonomous Features Are Outpacing Full Autonomy
The race to achieve full autonomy in the automotive industry has been a hot topic for years, with companies like Tesla, Waymo, and General Motors vying to become the first to offer fully self-driving cars to the market. However, while the potential benefits of full automation are undeniable, it seems that semi-autonomous features are currently getting the upper hand. In fact, many experts believe that semi-autonomous features are outpacing full autonomy, and there are several reasons behind this trend. In this article, we’ll explore why semi-autonomous features are taking the lead and what this means for the future of autonomous driving.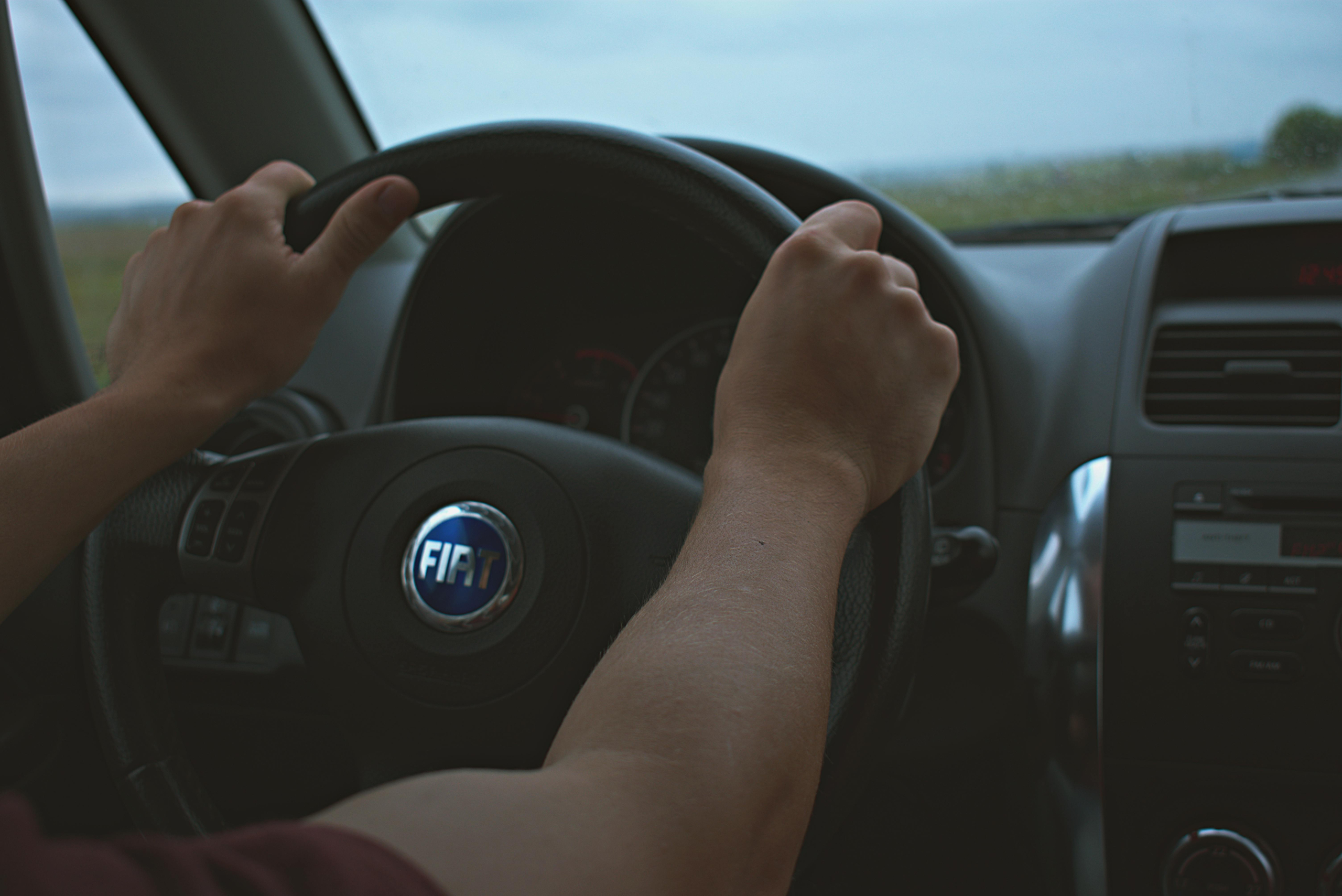
The Definition of Autonomy
Before diving into why semi-autonomous features are gaining popularity, it’s important to first understand what autonomy really means in the context of driving. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines six levels of driving automation, ranging from no automation (Level 0) to full automation (Level 5). At Level 5, a vehicle is capable of navigating all roads and traffic conditions without any human intervention, while at Level 0, a driver controls the entire driving task manually. Partial automation, or semi-autonomous features, fall somewhere in between these two extremes.
Semi-Autonomous vs. Full Autonomous Features
So, what’s the difference between semi-autonomous and full autonomous features? Semi-autonomous features, also known as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), are designed to assist a driver in controlling the vehicle, but they still require some level of human intervention. Examples of semi-autonomous features include adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking. On the other hand, full autonomous features take over the entire driving task, eliminating the need for human input.
The Hype Around Full Autonomy
When Tesla first introduced their Autopilot feature in 2014, it caused a stir in the automotive industry. Suddenly, the idea of fully self-driving cars seemed not only possible but imminent. Other big players like Waymo and General Motors quickly followed suit and began heavily investing in developing their own autonomous technology. The promise of a future where cars can drive themselves and eliminate the possibility of human error was incredibly appealing, and the hype surrounding full autonomy grew.
The Challenges of Full Autonomous Driving
However, as the industry delved deeper into the development of full autonomous driving, it became clear that there were significant challenges to overcome. One major obstacle was the technology itself. While semi-autonomous features rely on sensors and cameras to assist in driving tasks, a completely autonomous vehicle must be able to analyze and respond to any road and traffic situation with the same – or even better – accuracy than a human.
Another challenge is public perception and trust. Despite the potential of full autonomy to reduce accidents and fatalities, many people are still hesitant and even fearful of handing over complete control to a machine. Recent incidents involving autonomous vehicles have only added to these concerns, making it more difficult for companies to fully test and introduce their technology to the market.
The Advantages of Semi-Autonomous Features
While full autonomy still holds significant potential, it’s clear that semi-autonomous features have several advantages that make them a more feasible option for the present. One of the most significant benefits of semi-autonomous features is their ability to improve safety while still allowing for human input. Features like adaptive cruise control and lane keep assist can help prevent accidents by alerting drivers to potential hazards and helping them maintain safe driving habits.
Additionally, semi-autonomous features are often more affordable and easier to implement. With full autonomy, vehicles require a complete overhaul of their current systems and infrastructure, which can be a time-consuming and expensive process. On the other hand, semi-autonomous features can be integrated gradually and are already available in many new cars today.
The Evolution Towards Full Autonomy
Despite the current dominance of semi-autonomous features, many experts and industry leaders still believe that full autonomy is the inevitable future of driving. However, the path to get there may take longer than originally anticipated, and the evolution towards full autonomy will be gradual. In the meantime, semi-autonomous features will continue to improve and gain traction, offering tangible advantages to drivers in terms of comfort and safety.
In conclusion, while the potential of full autonomous driving cannot be ignored, it’s clear that semi-autonomous features are currently paving the way for the future. Their safety benefits, easier implementation, and lower cost make them a more practical solution for the present, and as technology continues to advance, the eventual transition to full autonomy will be smoother and more successful. So, while full autonomy may be the end goal, it seems that semi-autonomous features are the key to getting there.